Windows Vista - Defragmenting via the command line
 As in the previous version Windows XP is also in Windows Vista contain the defragmentation tool.
As in the previous version Windows XP is also in Windows Vista contain the defragmentation tool.
However, the one included in Vista works defragmentation more in the background and does its job inconspicuously and time-controlled.
The visual representation during the defragmentation is also no longer available, which means that the interested user does not receive any information about the actual degree of fragmentation of his hard disk.
If you want to know what the actual degree of fragmentation is, you can go to the much more informative one Command line tool evade...
Background - what exactly is fragmentation?
Fragmentation of a hard drive occurs over time as files are saved, modified, or deleted. These changes are often saved in a different location on the hard drive than the original file. Over time, the file and the hard drive become fragmented, i.e. stored across large areas of the hard drive, and the access times become longer because in order to open a file, the hard drive's read head has to access many different locations in order to read the corresponding file.
defragmenting
The defragmentation program can be manually bypassed over the schedule
Start> All Programs> Accessories> System Tools> Defragmentation
to be started.
As you can see, no information about the degree of fragmentation is given.
So let's take a look at defragmentation from the command line.
Defragment via the command line
First we start the Command line (Command prompt) with administrator rights.
Go to Home and give cmd into the search box above the start button.
The entry will now appear in the top left of the start menu cmd.exe
Click this with the right mouse button and select from the context menu "Execute as administrator".
In the now open window of the command prompt now enter the following command followed by Enter
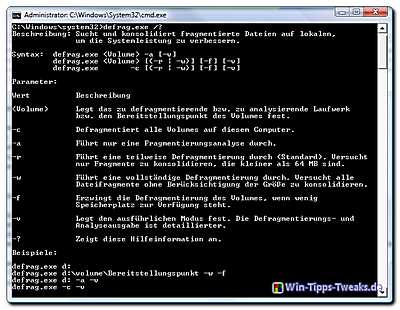
defrag.exe /?
This command shows all possible parameters including a brief explanation of its use.
See screenshot (click to enlarge)
For example:
To tell us the degree of fragmentation of Drive C: to display we use the following command:
defrag.exe C: -a -v
This command shows us fragmentation information from Drive C
The parameter -a pretends that only one analysis is performed.
The parameter -v Specifies verbose mode. The defragmentation and analysis output is more detailed.
It may take a while until all information has been read out, so be patient.
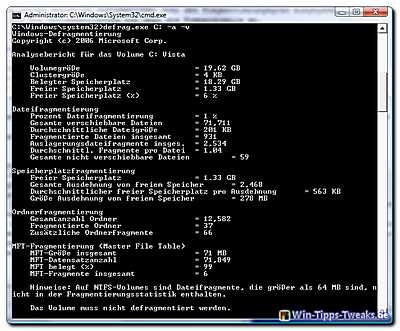
After the analysis, an output appears with detailed information on the
- File fragmentation
- Space fragmentation
- Folder fragmentation
- MFT fragmentation (MasteFileTable) and the
- Storage medium.
At the end of the output there is a note as to whether the volume should be defragmented or not.
You can find an example of this issue in the screenshot below (click to enlarge).
Please also note that file fragments on NTFS formatted volumes which are larger than 64 MB are not included in the fragmentation statistics.
A few examples:
In order to complete and particularly thorough defragmentation of drive C: we use the following parameters:
defrag.exe C: -v -w -f
A thorough one Defragment all existing drives (volumes)
defrag.exe -c -v -w -f
Note:
The defragmentation can take a long time, depending on the size and number of the volumes, and it can put a lot of strain on the computer, so it makes sense to do this at times when the work is not impaired and the defragmentation can do its job undisturbed.
| Transparency: | This article may contain affiliate links. These lead directly to the provider. If a purchase is made through this, we receive a commission. There are no additional costs for you! These links help us to refinance the operation of win-tipps-tweaks.de. |
This tip comes from www.win-tipps-tweaks.de
© Copyright Michael Hille
Warning:
Using Registry Editor or its tips incorrectly can cause serious system problems that may require you to reinstall your operating system. Tampering with the registry files and using the tips is at your own risk.